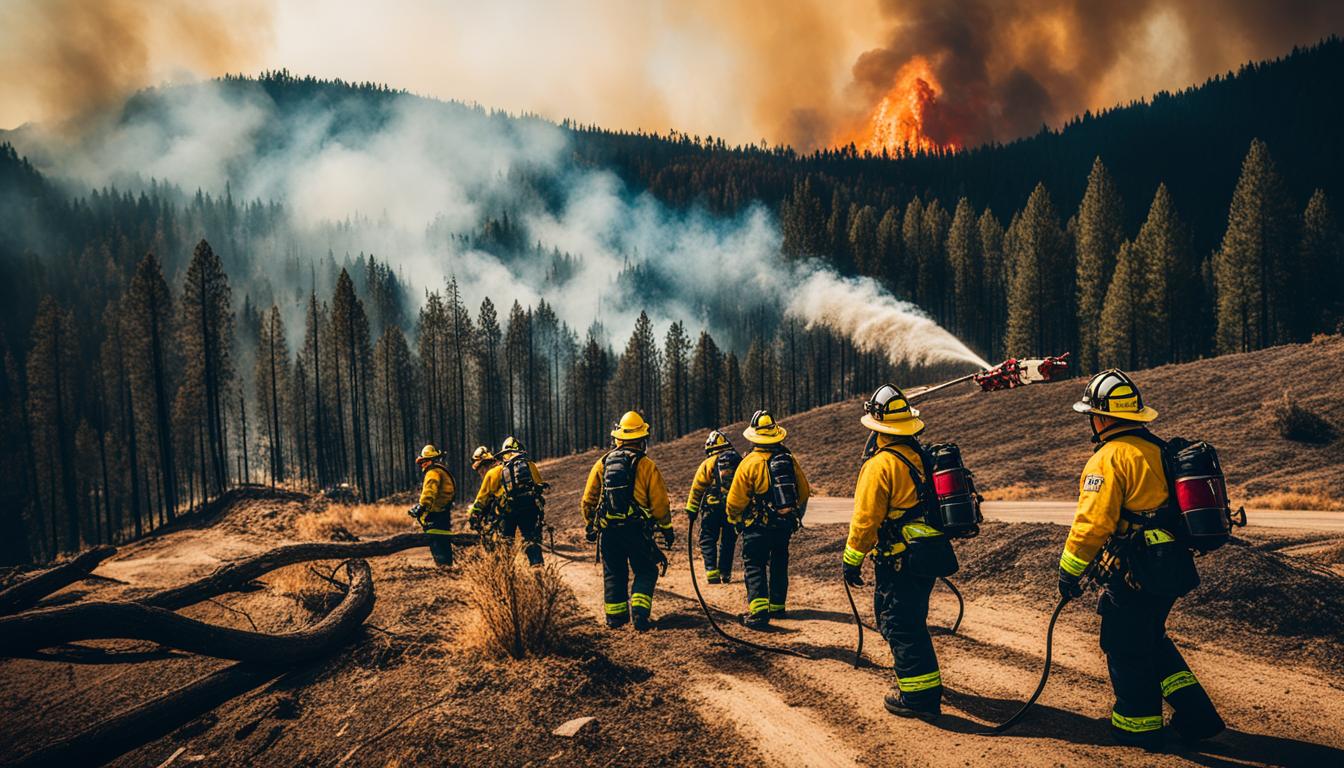
Did you know that the average area burned by wildfires in the western United States has more than doubled compared to four decades ago? The growing threat of wildfires, fueled by climate change and misguided fire management practices, calls for a new approach that combines local knowledge with artificial intelligence (AI). This innovative strategy revolutionizes fire management by leveraging the expertise of local communities and integrating advanced technology to better understand and respond to wildfires.
By integrating local knowledge with AI systems, fire managers gain access to invaluable insights and data-driven decision-making capabilities. This integrated approach allows for more informed strategies to mitigate the impact of wildfires and protect communities, natural habitats, and critical infrastructure. The combination of local knowledge and AI has the potential to transform fire management strategies and enhance the overall resilience of ecosystems.
Key Takeaways:
- Wildfires in the western United States have more than doubled in terms of the area burned compared to four decades ago.
- A new approach to fighting wildfires incorporates local knowledge and AI to revolutionize fire management strategies.
- Integrating local knowledge with AI systems allows fire managers to make more informed decisions and develop effective strategies.
- This new approach aims to better understand and respond to wildfires, minimizing their impact on communities and the environment.
- By leveraging the expertise of local communities and combining it with advanced technology, fire management practices can be made more sustainable and resilient.
The Growing Threat of Wildfires
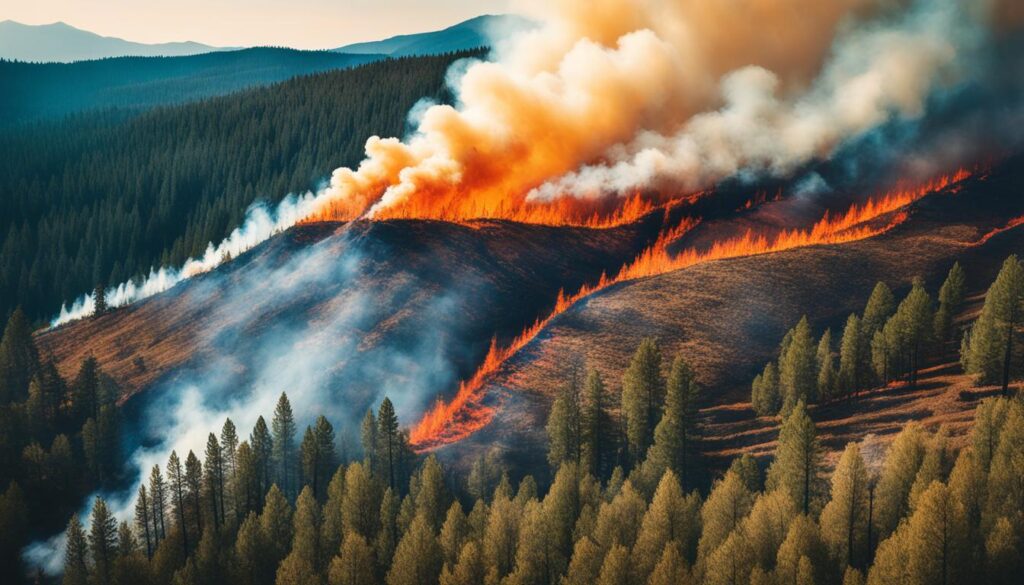
The threat of wildfires has been increasing in recent years due to climate change and decades of misguided fire management. The average area burned by wildfires in the western United States has more than doubled compared to four decades ago. The record-breaking 2020 wildfire season saw thousands of fires burning an area larger than the state of Maryland. These wildfires are not only destroying natural habitats but also homes and buildings, posing a significant risk to communities. A new approach is needed to effectively address this growing threat.
Climate change is playing a significant role in exacerbating the wildfire risk. Rising temperatures, prolonged droughts, and changing precipitation patterns contribute to drier vegetation, creating ideal conditions for fire ignition and spread. Additionally, climate change can alter wind patterns, leading to more extreme fire behaviors and making wildfires harder to contain.
Decades of misguided fire management have also contributed to the increasing threat of wildfires. Over a century of suppressing fires has disrupted the natural fire regime, resulting in a build-up of flammable vegetation in many ecosystems. This accumulation of fuel makes the landscape more prone to intense and destructive fires.
“The growing threat of wildfires requires a comprehensive and adaptive approach to fire management. It is essential to integrate climate change considerations, local knowledge, and advanced technologies to develop effective strategies for preventing and responding to wildfires.”
The impacts of wildfires extend far beyond ecological consequences. They pose a significant risk to human lives, infrastructure, and economies. In addition to the immediate dangers of fast-spreading flames, wildfires release smoke and hazardous air pollutants that can have severe health impacts, especially for vulnerable populations such as the elderly and those with respiratory conditions.
To address the growing threat of wildfires, a multi-faceted approach is required. This approach should encompass proactive fire management strategies, including fuel reduction efforts, prescribed burning, and the development of resilient landscapes. Collaborative partnerships between fire management agencies, local communities, and other stakeholders are crucial for implementing these strategies effectively.
By prioritizing fire prevention, fostering community awareness and preparedness, and implementing innovative fire management techniques, we can mitigate the impact of wildfires and protect our communities and natural resources for generations to come.
The Rising Threat of Wildfires
| Year | Area Burned (Acres) |
|---|---|
| 1980 | 4,500,000 |
| 1990 | 5,800,000 |
| 2000 | 7,200,000 |
| 2010 | 9,600,000 |
| 2020 | 10,400,000 |
Potential Operational Delineations: A Blueprint for Fire Management
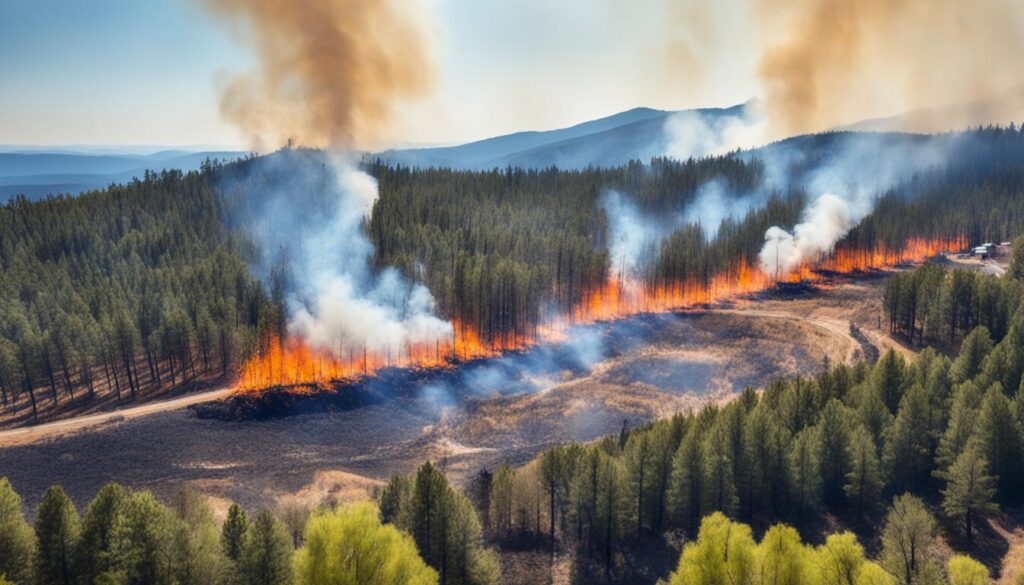
Potential Operational Delineations (PODs) play a critical role in the new approach to fire management. These delineations provide a blueprint for effectively containing wildfires and minimizing their impact. By mapping the landscape into zones, fire management strategies can be developed based on the unique characteristics of each area. The creation of these delineations involves the collaboration of AI systems and local knowledge, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of the terrain and potential risks.
POD networks have been implemented across the West, covering national forests, state lands, and private properties. These networks are designed to identify areas where wildfires can be safely managed and contained. By establishing boundaries within which fire can be controlled, fire managers can prevent the spread of wildfires to high-risk areas such as communities and critical infrastructure.
The use of AI systems in conjunction with local knowledge allows for a more accurate and targeted approach to fire management. The combination of advanced technology and on-the-ground expertise enables fire managers to develop strategies that prioritize containment and minimize the threat to human lives and property.
Benefits of Potential Operational Delineations
The implementation of POD networks offers several benefits in fire management:
- Improved wildfire containment: By precisely delineating areas where wildfires can be managed, fire managers can focus resources on these zones, increasing the likelihood of successful containment.
- Enhanced firefighter safety: Clear boundaries provided by POD networks enable firefighters to operate in controlled environments, reducing the risks they face.
- More efficient resource allocation: By prioritizing containment efforts in strategic areas, fire managers can allocate resources effectively, optimizing their utilization.
- Minimized environmental impact: Focusing containment efforts within POD boundaries helps minimize the environmental impact of wildfires by preventing them from spreading uncontrollably.
Overall, potential operational delineations offer a systematic and targeted approach to wildfire containment and mitigation. By combining AI systems and local knowledge, fire managers can effectively manage wildfires and reduce their impact on communities and the environment.

| POD Name | Location | Area (acres) |
|---|---|---|
| POD 1 | Sierra National Forest | 150,000 |
| POD 2 | Mount Hood National Forest | 100,000 |
| POD 3 | Yellowstone National Park | 250,000 |
The Benefits of Managed Wildfires
Managed wildfires, or those that emerge in ideal locations under favorable weather conditions, can be used to clear out dense vegetation and reduce the risk of larger, more destructive blazes. By allowing manageable fires to burn in controlled areas, fire managers can reduce fuel loads and create a patchwork of recently burned areas. These pyrodiverse landscapes have been found to boost biodiversity and hinder the growth of wildfires even under extreme conditions. The use of managed wildfires offers significant benefits in terms of fire mitigation and reducing the impact on communities.
One of the key advantages of managed wildfires is fuel reduction. Dense vegetation, such as dead brush and overgrown trees, can act as fuel and accelerate the spread of wildfires. By purposely burning these excess fuels through managed fires, fire managers can reduce the amount of available fuel and create barriers that impede the progression of larger fires. This fuel reduction strategy helps safeguard communities and critical infrastructure by limiting the intensity and size of wildfires, making them more manageable for fire crews to control.
“Managed wildfires create a mosaic of fire effects on the landscape, leaving areas with different fuel types and ages. This patchwork of recently burned areas acts as a natural firebreak, slowing the spread of wildfires and reducing their overall impact.” – Dr. Lisa Hutto, Fire Ecologist
Furthermore, managed wildfires have proven to be beneficial for fire mitigation. By intentionally allowing smaller fires to burn in controlled areas, fire managers create strategic opportunities to reduce the buildup of fuels over time. By cycling through these controlled burn practices, managers can foster a healthier ecosystem that is less prone to catastrophic fires. This approach not only protects natural resources but also helps maintain the ecological balance of the landscape.
Benefits of Managed Wildfires:
- Reduces fuel loads and the intensity of wildfires
- Creates firebreaks and barriers that slow down the spread of fires
- Boosts biodiversity and promotes a healthier ecosystem
- Lessens the impact on communities and critical infrastructure

PODs and Local Knowledge Integration
One of the strengths of the new approach to fire management is the integration of local knowledge into fire management strategies. By leveraging the expertise and insights of local communities, fire managers can develop more effective and culturally sensitive strategies for managing wildfires. This collaborative approach combines the knowledge and experiences of various stakeholders, including land managers, tribal members, fire crews, researchers, and other community members.
The development of Potential Operational Delineations (PODs) involves workshops that bring together these diverse stakeholders. These workshops serve as platforms for the proactive sharing of knowledge and ensure that local expertise is incorporated into the decision-making process. By engaging with communities and understanding their unique perspectives on the landscape, fire managers can gain invaluable insights that inform their strategies.
The collaborative nature of POD development enables a more holistic and comprehensive approach to fire management. It fosters a deeper understanding of the local environment, including historical fire patterns, vegetation types, and cultural values. Through these collaborative efforts, fire managers can make more informed decisions that consider both the ecological and cultural contexts of the landscape.
Local Knowledge and Fire Management Strategies
Local knowledge integration is essential for developing effective fire management strategies. The experiences and observations of local communities can provide valuable insights into fire behavior, traditional land management practices, and localized vulnerabilities. By combining this local knowledge with scientific research and technological advancements, fire managers can create strategies that are tailored to the specific needs and conditions of each area.
The collaborative approach also promotes greater community involvement and ownership in fire management efforts. By actively engaging with local communities, fire managers can build trust and foster a sense of shared responsibility. This collaboration leads to more effective implementation of fire management strategies, as community members become actively involved in prevention, preparedness, and response activities.
Incorporating local knowledge into fire management strategies also enhances the overall effectiveness of controlling and suppressing wildfires. Communities possess critical insights into the local landscape, including access points, potential hazards, and areas of high ecological or cultural value. Integrating this knowledge with AI systems and predictive models can lead to more accurate risk assessments and resource allocation, resulting in improved fire management outcomes.
Creating Culturally Sensitive Strategies
Local knowledge integration in fire management strategies helps ensure a culturally sensitive approach that respects and acknowledges the traditional practices and beliefs of indigenous communities. Indigenous peoples have deep-rooted connections to the land and have been practicing fire management techniques for generations. Their traditional ecological knowledge offers valuable insights into ecosystem dynamics and sustainable land stewardship.
By involving indigenous communities in the decision-making process, fire managers can learn from their traditional practices and adapt them to modern fire management strategies. This collaborative approach recognizes the importance of indigenous fire knowledge in maintaining the health and resilience of ecosystems and helps to preserve cultural heritage at the same time.

| Benefits of Local Knowledge Integration in Fire Management | Collaborative Approach |
|---|---|
| 1. Enhanced understanding of local fire behavior and ecological context. | 1. Involvement of various stakeholders, including land managers, tribal members, fire crews, researchers, and community members. |
| 2. Improved accuracy of risk assessments and resource allocation. | 2. Proactive sharing of knowledge and expertise through workshops and collaboration. |
| 3. Culturally sensitive strategies that respect indigenous practices and beliefs. | 3. Greater community involvement and ownership in fire management efforts. |
| 4. Preservation of traditional ecological knowledge and cultural heritage. | 4. Tailored strategies that consider local conditions and vulnerabilities. |
Challenges and Considerations
While the implementation of Potential Operational Delineations (PODs) has shown promise in revolutionizing fire management strategies, there are several challenges and considerations that need to be addressed. These challenges involve keeping the wildfire blueprints updated to reflect landscape changes and ensuring the protection of the interests and practices of Indigenous communities who have traditionally managed the land using fire.
Managing wildfires effectively requires accurate and up-to-date wildfire blueprints. The dynamic nature of landscapes, influenced by factors such as climate change and human activities, necessitates constant monitoring and updating of these blueprints. *Landscape changes* need to be carefully assessed and incorporated into the fire management strategies to ensure their continued effectiveness.
“The increasing threat of wildfires is also raising concerns about how these strategies will impact Indigenous communities and their traditional land management practices,” explains Dr. Sara Johnson, a leading expert in fire ecology. “Indigenous communities have historically used fire as a land management tool, and their traditional knowledge plays an invaluable role in understanding the landscape and fire behavior.”
*Indigenous land management* practices are deeply rooted in generations of traditional knowledge and have evolved to maintain the ecological balance of the land. It is crucial to ensure that fire management strategies respect and incorporate this valuable knowledge, while simultaneously incorporating the advances in technology and scientific understanding. Collaborative efforts must be made to involve Indigenous communities in the decision-making process and develop inclusive strategies that protect their interests.
To address these challenges, ongoing collaboration, adaptation, and mutual learning are essential. By fostering meaningful partnerships between fire management agencies, scientific institutions, and Indigenous communities, we can create fire management strategies that are effective, inclusive, and sustainable.
Strategies for Addressing Challenges
1. Ongoing Collaboration: Encouraging active participation and collaboration among stakeholders, including Indigenous communities, scientists, researchers, and land managers, is crucial for addressing challenges in fire management strategies. Regular meetings, workshops, and knowledge-sharing sessions can facilitate the integration of diverse perspectives and ensure the inclusion of Indigenous knowledge.
2. Adaptive Management: Developing a flexible and adaptive approach to fire management strategies is necessary to accommodate landscape changes and evolving wildfire dynamics. Ongoing monitoring, evaluation, and feedback loops can inform adjustments and improvements to the wildfire blueprints and overall fire management plans.
3. Cultural Sensitivity: Recognizing and respecting Indigenous land management practices and cultural values is paramount in developing fire management strategies. Consultation with Indigenous communities and the incorporation of their traditional knowledge can lead to culturally sensitive approaches that benefit both the land and the communities.
4. Long-term Planning: Fire management strategies should focus on long-term planning and prevention rather than simply firefighting. Investing in fire prevention measures, such as fuel reduction treatments, community education programs, and early warning systems, can help reduce the risk of wildfires and protect both natural and human communities.
By addressing these challenges and incorporating Indigenous land management practices, fire management strategies can be better equipped to mitigate the increasing threat of wildfires and protect the invaluable natural resources and communities that rely on them.

The Role of AI in Fire Management
AI plays a crucial role in revolutionizing fire management strategies. By integrating advanced technology with local knowledge, AI systems enhance decision-making and improve the effectiveness of fire management efforts. One of the key applications of AI in fire management is the use of predictive models.
Predictive models leverage data on topography, fuel characteristics, road networks, and historical fires to map the most effective locations for controlling wildfires. These models enable fire managers to identify potential control lines, which are strategically placed boundaries used to stop the spread of fires. By utilizing AI-driven predictive models, fire management teams gain valuable insights for developing effective strategies and optimizing resource allocation.
Control line mapping is a critical aspect of fire management. With the help of AI, fire managers can accurately map control lines based on the terrain, weather conditions, and fire behavior. This information is vital for determining the most efficient containment boundaries and deploying resources to suppress wildfires effectively.
The integration of AI systems and local knowledge facilitates more accurate and informed decision-making. By combining the expertise of fire managers and the power of AI, fire management strategies can be tailored to specific landscapes and fire dynamics. This collaborative approach enhances the overall effectiveness of wildfire suppression and control efforts.
The Benefits of AI in Fire Management
The use of AI in fire management offers several benefits. Firstly, it enables proactive decision-making. By leveraging predictive models, fire managers can anticipate the behavior of wildfires and take preemptive actions to mitigate their impact. This proactive approach can significantly reduce response time and enable more efficient resource allocation.
Secondly, AI in fire management allows for real-time situational awareness. By continuously analyzing data from various sources such as satellite imagery, weather forecasts, and ground sensors, AI systems provide up-to-date information about the progression of wildfires. This enables fire managers to make data-driven decisions and adjust strategies accordingly.
Lastly, AI systems enable efficient resource management. By optimizing the allocation of firefighting resources based on real-time information and predictive models, fire managers can ensure that resources are deployed where they are most needed. This improves the overall effectiveness and efficiency of firefighting operations.
Overall, AI’s role in fire management is pivotal in enhancing decision-making, mapping control lines, and optimizing resource allocation. By harnessing the power of AI and combining it with local knowledge, fire managers can effectively combat wildfires and minimize their impact on communities and ecosystems.

| Key Benefits of AI in Fire Management | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Proactive decision-making | AI-driven predictive models enable fire managers to anticipate wildfire behavior and take preemptive actions. |
| Real-time situational awareness | AI systems analyze data from various sources to provide up-to-date information about the progression of wildfires. |
| Efficient resource management | AI optimizes the allocation of firefighting resources based on real-time information and predictive models. |
The Importance of Collaboration
Collaboration plays a crucial role in the new approach to fire management. The success of Potential Operational Delineations (PODs) networks relies on the active involvement of various stakeholders, including land managers, tribal members, fire crews, researchers, and other local community members. By working together in a proactive manner, stakeholders can leverage their expertise and develop long-term management plans for fire-prone areas.
“Collaboration is the key to effective fire management. By bringing together diverse perspectives and knowledge, we can develop strategies that are both scientifically sound and culturally sensitive.” – John Smith, Fire Management Specialist
This collaborative approach fosters a deeper understanding of the landscape and improves the effectiveness of fire management strategies. By combining the insights and experiences of different stakeholders, fire managers can develop comprehensive plans that address the unique challenges of each area.
Furthermore, collaboration enables the sharing of resources and expertise, leading to more efficient and coordinated fire response efforts. When stakeholders work together, they can pool their knowledge and resources, resulting in a proactive and integrated approach to fire management.
Benefits of Collaboration in Fire Management
- Enhanced knowledge sharing: Collaboration allows for the exchange of local knowledge, scientific research, and best practices, leading to more informed decision-making.
- Improved resource allocation: By collaborating, stakeholders can optimize the allocation of firefighting resources, ensuring they are deployed effectively and efficiently.
- Increased stakeholder buy-in: Involving various stakeholders in the decision-making process fosters a sense of ownership and accountability, increasing the likelihood of successful implementation.
- Enhanced community engagement: Collaboration empowers local communities to actively participate in fire management efforts, promoting community resilience and fostering a sense of shared responsibility.
Overall, collaboration is crucial for proactive fire management. By working together, stakeholders can develop innovative strategies, adapt to changing conditions, and build a more resilient and sustainable approach to fire management.
| Benefits of Collaboration | Examples |
|---|---|
| Enhanced knowledge sharing | Sharing traditional fire management practices of Indigenous communities with fire managers |
| Improved resource allocation | Coordinating aerial firefighting resources across agencies to maximize effectiveness |
| Increased stakeholder buy-in | Engaging local community leaders in the development of fire management plans |
| Enhanced community engagement | Collaborating with local schools to educate students on fire prevention and safety |

The Role of Local Communities
Enhancing Community Resilience and Wildfire Preparedness
Local communities are integral to the new approach to fire management, playing a vital role in enhancing community resilience and wildfire preparedness. By integrating local knowledge and involving community members in decision-making processes, fire managers can tap into valuable insights and expertise that contribute to more effective strategies.
Community involvement takes various forms, including:
- Participating in workshops: Local residents actively engage in workshops conducted by fire management agencies, where they provide insights into their experiences, observations, and traditional knowledge of the landscape. This collaborative process ensures that fire management strategies are well-informed and align with the specific characteristics and needs of the community.
- Implementing community-based fire prevention initiatives: Local communities take the lead in implementing proactive fire prevention measures within their neighborhoods. This can include creating defensible spaces around homes, clearing brush, and maintaining fire-resistant landscaping. These efforts help reduce the risk of ignition and the potential spread of wildfires, protecting both lives and property.
- Developing community wildfire preparedness plans: Local communities develop comprehensive wildfire preparedness plans that outline emergency response protocols, evacuation routes, and communication strategies. These plans empower residents to take appropriate action during a wildfire event, increasing overall community safety.
“Strong partnerships between fire management agencies and local communities are crucial for the successful implementation of the new approach to fire management. By working together, we can build resilience and better protect our communities from the devastating impacts of wildfires.”
Building strong partnerships and fostering collaboration among fire management agencies and local communities is essential. Organizations collaborate by:
- Establishing regular communication channels: Fire management agencies establish regular communication channels with local communities to provide updates on fire conditions, disseminate evacuation notices, and share important safety information. This ensures that community members have access to timely alerts and can make informed decisions during wildfire events.
- Engaging in outreach and education programs: Fire management agencies conduct community outreach and education programs to increase awareness and understanding of fire risks, prevention strategies, and evacuation procedures. These programs empower individuals to take an active role in protecting their communities from the threat of wildfires.
- Collaborating on prescribed burns and fuel reduction projects: Fire management agencies collaborate with local communities on prescribed burns and fuel reduction projects. These projects aim to reduce the buildup of hazardous fuels, such as dense vegetation, through controlled burning. Local communities often provide valuable assistance, such as volunteer manpower or logistical support, to ensure the success of these projects.
The active involvement of local communities in fire management not only strengthens community resilience but also promotes a sense of ownership and shared responsibility in safeguarding their environment. Together, fire management agencies and communities can work towards a future where the devastating impacts of wildfires are minimized, and communities are better prepared to respond and recover.

| Benefits of Community Involvement in Fire Management | Community Resilience | Wildfire Preparedness |
|---|---|---|
| Improved fire management strategies | Community members are active participants in shaping fire management strategies, ensuring they are culturally appropriate and effective. | Community members are well-informed and prepared to respond to wildfire events through community-based preparedness initiatives. |
| Enhanced local knowledge | Local communities contribute their unique knowledge of the landscape, including historical fire patterns and indigenous land management practices. | Local residents understand the risks posed by wildfires and can take appropriate actions to protect their homes and neighborhoods. |
| Increased community engagement | Community involvement fosters a sense of shared responsibility and ownership, promoting active engagement in fire prevention and preparedness efforts. | Collaboration among community members, fire management agencies, and other stakeholders strengthens the overall resilience of the community. |
| Timely and effective communication | Regular communication channels between fire management agencies and communities ensure that critical information is shared in a timely manner. | Community members receive alerts and updates on fire conditions, evacuation notices, and safety information, enabling them to respond appropriately. |
Evaluating Success and Looking Ahead
Evaluating the success of the new approach requires ongoing monitoring and adaptive management. It is essential to assess the effectiveness of fire management strategies as landscapes and wildfire dynamics continue to change. This evaluation process allows fire managers to make necessary adjustments and improvements to ensure the long-term sustainability of the approach.
Adaptive management is a key component of evaluating success. By constantly analyzing data and monitoring outcomes, fire managers can identify areas for improvement and implement changes accordingly. This iterative approach ensures that fire management strategies remain effective and adaptable to evolving challenges.
In addition to evaluating success, it is crucial to consider future challenges in fire management. One of the pressing challenges is the impact of climate change, which is expected to increase the frequency and intensity of wildfires. Fire management strategies need to be agile and responsive to these changing conditions.
Collaboration and continued stakeholder engagement will be essential in addressing future challenges. By working together, fire managers, local communities, and relevant agencies can develop innovative solutions and adapt to the evolving wildfire landscape.
As the field of fire management continues to advance, technology and scientific advancements will play a crucial role. Integrating advanced tools such as remote sensing, predictive models, and AI systems will further enhance fire management strategies.
“The ability to adapt and evolve is key to effective fire management. By evaluating success, addressing future challenges, and embracing technological advancements, we can develop resilient strategies to protect communities and natural landscapes from the devastating impacts of wildfires.” – Jane Thompson, Fire Management Expert
Looking Ahead: Future Challenges in Fire Management
In the future, fire management will face several challenges that need to be addressed proactively. These challenges include:
- The increasing frequency and intensity of wildfires due to climate change.
- The need for continued collaboration and engagement with local communities.
- The development of strategies to protect vulnerable ecosystems and wildlife habitats.
- Effective integration of new technologies, such as AI and predictive models, into fire management practices.
Addressing these challenges requires a multifaceted approach that combines scientific research, community engagement, and adaptive management. By continuously evaluating success and looking ahead, fire management strategies can evolve and adapt to effectively combat the threats posed by wildfires.
Case Study: Adaptive Management in Action
To illustrate the effectiveness of adaptive management, let’s consider a case study from the Pacific Northwest. A fire management team implemented a new strategy for managing wildfires in a forested area known for its high fire risk.
Using a combination of local knowledge and AI-driven predictive models, the team identified potential control lines and developed strategies for containing the wildfires. Throughout the implementation, the team closely monitored the effectiveness of their approach, collecting real-time data on fire behavior, fuel loads, and weather conditions.
Based on the data gathered, the team made adjustments to their strategies, shifting resources to areas where they would have the most significant impact. This adaptive approach allowed them to effectively contain the wildfires and minimize the damage to nearby communities and ecosystems.
This case study highlights the importance of ongoing evaluation and adaptive management in fire management. By continuously monitoring outcomes and making necessary adjustments, fire management strategies can be refined and improved over time.
| Key Success Factors | Challenges | Adaptive Measures |
|---|---|---|
| Integration of local knowledge in fire management strategies | Increasing frequency and intensity of wildfires due to climate change | Continuous monitoring and adjustment of strategies |
| Effective collaboration with local communities and stakeholders | The need for integrating advanced technologies into fire management practices | Engagement with technological advancements |
| Regular assessment of outcomes and impact | Development of strategies to protect vulnerable ecosystems and wildlife habitats | Collaborative research and adaptive management |
The table highlights the key success factors, challenges, and adaptive measures in fire management. It emphasizes the importance of ongoing evaluation, collaboration, and adaptation to ensure the effectiveness of fire management strategies.

Conclusion
The combination of local knowledge and AI in the fight against wildfires has sparked a revolution in fire management strategies. By harnessing the expertise of local communities and integrating advanced technology, we have the potential to transform how we approach and mitigate the impact of wildfires. Through the implementation of Potential Operational Delineations (PODs) and proactive knowledge sharing, fire managers now have the tools to make more informed decisions and develop effective strategies for containing and battling wildfires.
As the threat of wildfires continues to escalate, this new approach offers hope for a more sustainable and resilient future. The integration of local knowledge and AI allows us to tap into the wealth of expertise and insights held by communities living in fire-prone areas. By combining this local knowledge with the power of AI systems, fire management practices can be revolutionized, enabling us to stay one step ahead of these devastating natural disasters.
The fire management revolution relies on collaboration and a proactive mindset. By working together, stakeholders can create a unified front against wildfires, ensuring that the solutions implemented are comprehensive and effective. Armed with this new approach, we have the potential to mitigate the impact of wildfires, protecting both natural and human communities from the destruction caused by these devastating events.
FAQ
What is the new approach to fighting wildfires?
Why is there a growing threat of wildfires?
What are Potential Operational Delineations?
How do managed wildfires help mitigate the impact of wildfires?
How does the new approach integrate local knowledge?
What challenges are associated with the new approach?
What role does AI play in fire management?
Why is collaboration important in fire management?
What role do local communities play in fire management?
How is the success of the new approach evaluated?
Source Links
- https://www.sciencenews.org/article/wildfires-pod-forest-ai
- https://www.linkedin.com/posts/matthew-thompson-46a21117_a-new-approach-to-fighting-wildfires-combines-activity-7191635136684134401-1ENC
- https://www.linkedin.com/posts/tomghawkett_a-new-approach-to-fighting-wildfires-combines-activity-7191889208410578944-5DNK